Categories
What is the difference between 2, 3 and 4 wire RTD temperature sensing?
March 31 , 2023What is the difference between 2, 3 and 4 wire RTD temperature sensing?
The difference between 2, 3 and 4 wire RTD temperature sensing is the accuracy of the measurement. Using 2 Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) sensing provides good accuracy (possibly), 3-wire sensing provides better accuracy, and 4-wire sensing provides the best accuracy.
There is also the option of using a Wheatstone bridge topology to improve the performance of 2-wire and 3-wire RTDs. This FAQ first reviews the basics of RDT devices, examines the trade-offs between 2-, 3-, and 4-wire sensing, and concludes with a brief introduction to Wheatstone bridges and temperature sensing.
In addition to RTDs, designers can choose from thermistors and thermocouples. RTDs are a particularly good choice in many applications because of their fast response times, repeatability, and excellent sensitivity up to several hundred µV/°C. RTDs can be used over a wide range from -200°C to +800°C and have nearly linear behavior.
RTDs can be made from a variety of materials, including nickel, copper, and platinum. While platinum resistance thermometers (PRTDs) are more expensive, other metals are not widely used because they are not as stable or reproducible as PRTDs. In addition, PRTDs are not affected by corrosion or oxidation. In industrial, medical, and aerospace applications where accuracy and repeatability over the -200 to +800 °C temperature range are important, PRTDs are the best choice.
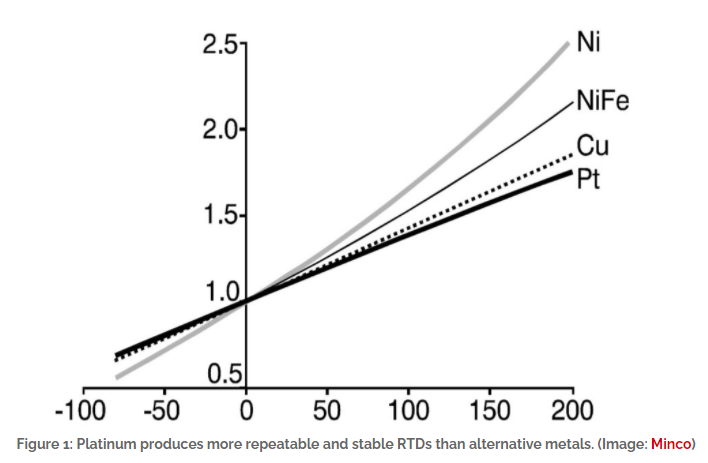
The development of modern PRTD standards, such as IEC 60751 and ASTM 1137, allow a wide range of sensor interchangeability between systems based on specified tolerances and temperature coefficients. These standards make it easy to replace sensors with sensors from the same or different manufacturers while maintaining rated performance with minimal redesign or recalibration of the system. However, designers need to be aware that IEC 60751 has been revised in 2008 and again in 2022.IEC 60751:2022 introduces several significant technical changes.
The three most common PRTDs are the PT100, PT500, and PT1000, which have resistances of 100 Ω, 500 Ω, and 1000 Ω at 0 °C, respectively. The PT1000 is by far the most common type of PRTD. RTDs are available in 2-wire, 3-wire, and 4-wire configurations.
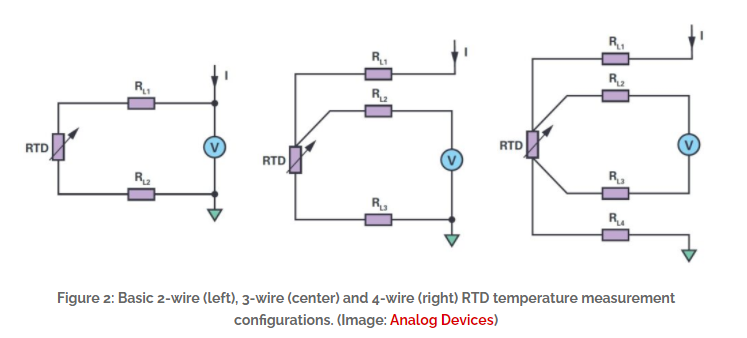
The simplest implementation has a 2-wire RTD configuration and two leads that provide excitation current (I) to the RTD to measure sensor voltage (and temperature). Because the resistance calculated for the circuit includes the resistance in the leads and connectors as well as the resistance in the RTD element, the results will always contain some degree of error. Even relatively low lead resistance (RL ) can cause significant measurement errors due to the low sensor resistance.
Using the shortest possible wire lengths and low-resistance connectors can reduce, but not eliminate, this error. Larger gauge wires with lower resistance can also help minimize errors. In cost-sensitive applications where high accuracy is not required, a 2-wire RTD configuration may be a viable option.