Categories
How PTC Thermistors Work
June 29 , 2023The thermistor will not operate for a long time; when the ambient temperature and current are in zone c, the heat dissipation power of the thermistor is close to the heat generation power, so the thermistor may or may not operate. When the thermistor is in the same ambient temperature, the action time is sharply shortened with the increase of current; the thermistor has a shorter action time and smaller maintenance current and action current when the ambient temperature is relatively high.
(1) ptc effect is a material with ptc (positivetemperaturecoefficient) effect, that is, the positive temperature coefficient effect, only refers to the resistance of this material will increase with the increase in temperature. Most metallic materials, for example, have the ptc effect. In these materials, the ptc effect is expressed as a linear increase in resistance with increasing temperature, which is commonly referred to as the linear ptc effect.
(2) Nonlinear ptc effect Materials that undergo a phase change exhibit a sharp increase in resistance of several to a dozen orders of magnitude along a narrow temperature range, the nonlinear ptc effect, which is exhibited by quite a few types of conductive polymers, such as polymeric ptc thermistors. These conductive polymers are very useful for the manufacture of overcurrent protection devices.
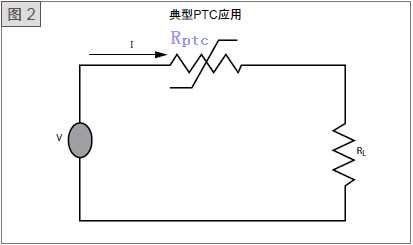
(3) Polymer ptc thermistors for overcurrent protection Polymer ptc thermistors, also often referred to as self-recovery fuses (hereinafter referred to as thermistors), are extremely suitable for use as overcurrent protection devices because of their unique positive temperature coefficient resistance characteristics. Thermistors are used like ordinary fuses, which are connected in series in a circuit.

Under normal operating conditions, the thermistor is close to room temperature and has low resistance, so it does not block the passage of current. However, when a fault occurs in the circuit resulting in overcurrent, the thermistor will increase in temperature due to increased heat generation power. When the temperature exceeds the switching temperature, the resistance of the thermistor increases rapidly and dramatically, causing the current in the circuit to decrease rapidly to a safe value.
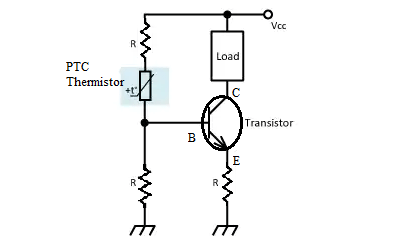
The polymer PTC thermistor has an adjustable switching temperature and can act as both over-temperature and over-current protection. By changing its own switching temperature, its sensitivity to temperature can be adjusted. For example, the KT16-1700DL size thermistor is suitable for overcurrent and overtemperature protection of Li-ion and NiMH batteries due to its low operating temperature.
The polymer PTC thermistor is a direct thermal, step type thermistor whose resistance change process is related to its own heat generation and heat dissipation. Under different ambient temperature and current conditions, the thermistor's maintenance current, action current and action time will be affected. When the ambient temperature and current are in a certain area, the thermistor's heating power is greater than the heat dissipation power, and the action will occur. When the ambient temperature and current are in another region , the heating power is less than the heat dissipation power, and the thermistor can be used repeatedly due to its recoverable property.
Typically, thermistors recover to a level of about 1.6 times their initial value between a few seconds and a few dozen seconds, at which point the thermistor's maintenance current also returns to its rated value and can be used again. The faster recovery thermistors tend to have smaller areas and thicknesses, while the slower recovery thermistors usually have larger areas and thicknesses. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the recovery time and heat dissipation conditions when using thermistors to ensure that they work properly during repeated use.
In general, thermistors have a low resistance and temperature sensitivity during normal operation and do not impede the normal operation of the circuit. However, when a circuit malfunction causes an overcurrent, the thermistor will heat up and dramatically increase its resistance, thereby limiting the current and providing overtemperature and overcurrent protection. Polymer PTC thermistors have an adjustable switching temperature and can be customized to meet your needs, while having good stability and overload capability.